Danger level
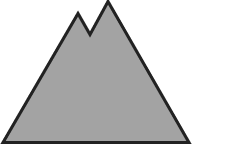
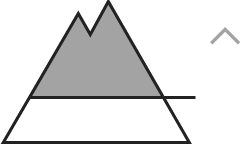
 | 2000m |
|  |
|  |

Assess with caution freshly generated snowdrifts in steep terrain
Avalanche danger above 2000m is moderate, below that altitude danger is low. Small to medium-sized slab avalanches can be triggered by one sole skier. Danger zones occur esp. on shady, ridgeline steep slopes and in wind-loaded gulliex and bowls. Size and frequency tend to increase in frequency with ascending altitude and during the course of the day. Danger of mostly small-sized glide-snow avalanches on grass-covered slopes or rocky plates still prevails. Therefore, caution urged below glide cracks.
Snowpack
Amounts of fresh snow from the new cold front: 5-10cm, less then expected. Winds moderate to brisk from westerly to northwesterly directions, generating fresh, often trigger-sensitive snowdrift accumulations. Bonding to the old snowpack surface deteriorates with ascending altitude. The below-average snowpack depths are generally well consolidated. Snowpack surfaces are highly varied: high altitude shady slopes are often still powdery, elsewhere there are breakable crusts, sometimes wind crusts are capable of bearing loads. On sunny slopes, a melt-freeze crust forms. Due to dropping temperatures, gliding snow activity will gradually recede.
Tendency
Avalanche danger levels will recede